반응형
프록시 패턴이란?
- 프록시 패턴의 특정 객체로의 접근을 제어하는 대리인을 제공하는 디자인패턴입니다.
- 프록시 패턴을 사용하면 생성하기 힘든 객체 또는 보안이 중요한 객체와 같이 접근을 제어하는 대리인 객체를 만들 수 있습니다.
- 프록시 패턴을 사용하게 되면 가상 프록시를 사용해서 생성하기 힘든 자원으로의 접근을 제어할 수 있으며 보호 프록시를 사용해서 접근 권한이 필요한 자원의 접근을 제어할 수 있습니다.
프록시 패턴의 종류
1. 원격 프록시
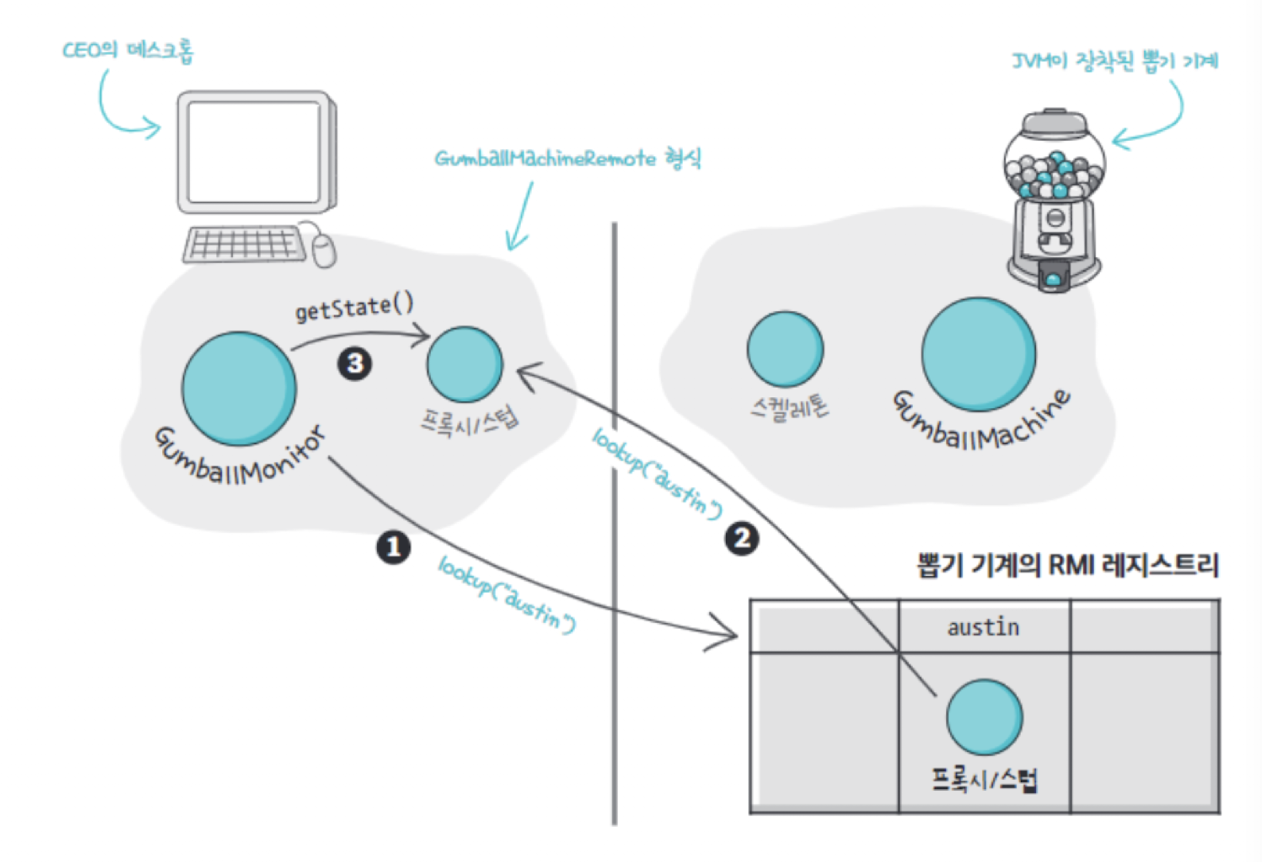
- 원격 프록시는 원격 개체의 로컬 대변자 역할을 수행하는것을 의미합니다.
- 로컬 대변자란 어떤 메소드를 호출하면 다른 원격 객체에게 그 메소드 호출을 전달해주는 객체를 로컬 대변자라고 합니다.
- 클라이언트 객체는 원격 객체가 가지고 있는 메소드를 호출 하는것처럼 행동합니다. 하지만 실제로로 로컬 힙에 들어있는 ‘프록시’ 객체의 메소드를 호출합니다.
- 네트워크 통신과 관련된 저수준 작업은 위의 프록시 객체에서 처리해준다.
원격 프록시 구현
public interface GumballMachineRemote extends Remote {
public int getCount() throws RemoteException;
public String getLocation() throws RemoteException;
public State getState() throws RemoteException;
}- 예시는 뽑기 기계를 원격으로 관찰하는 시스템을 만든다는 흐름으로 예시를 만들어보도록 하겠습니다.
- 먼저 GambleMachine을 관찰하기 위해 클라이언트가 전달할 행동들을 인터페이스화는 작업을 진행하겠습니다.
- 위의 인터페이스를 통해 GambleMachine을 호출하는 행동들을 정의한것입니다.
public interface State extends Serializable {
public void insertQuarter(); //동전 투입
public void ejectQuarter(); // 동전 반환
public void turnCrank(); //손잡이 회전
public void dispense(); //알맹이 반환
}- GambleMachine의 상태값을 가지고 있는 State 인터페이스입니다.
- 원격 객체에게 데이터를 전달할 때 데이터가 직렬화되어야 하므로 Serializable을 상속받습니다.
package com.example.designpattern.proxy.gumball;
public class NoQuarterState implements State {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2L;
//State 상태를 직렬화 하기위해 GumballMachine 자체를 직렬화하는것은 비효율적이기 때문에 Transient를 선언한다.
//Transient를 선언하게 되면 해당 필드는 직렬화하지 않는다.
//하지만 객체를 직렬화한 후에 해당 객체를 호춣하면 에러가 발생할 수 있다.
transient GumballMachine gumballMachine;
public NoQuarterState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("You inserted a quarter");
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getHasQuarterState());
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("You haven't inserted a quarter");
}
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("You turned, but there's no quarter");
}
public void dispense() {
System.out.println("You need to pay first");
}
public String toString() {
return "waiting for quarter";
}
}- 동전을 보유하지 않은 상태를 의미하는 NoQuarterState 객체이다.
- GumballMachine은 상태 패턴을 통해 구현되었기 때문에 객체의 상태에 맞게 등록된 행동이 수행된다.
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;
//원격 통신을 위한 java의 unicastRemoteObject를 상속받는다.
public class GumballMachine
extends UnicastRemoteObject implements GumballMachineRemote
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2L;
State soldOutState;
State noQuarterState;
State hasQuarterState;
State soldState;
State winnerState;
State state = soldOutState;
int count = 0;
String location;
//슈퍼 클래스에서 RemoteException을 던질수 있으므로 해당 생성자에도 RemoteException을 던질수 있어야한다.
public GumballMachine(String location, int numberGumballs) throws RemoteException {
soldOutState = new SoldOutState(this);
noQuarterState = new NoQuarterState(this);
hasQuarterState = new HasQuarterState(this);
soldState = new SoldState(this);
winnerState = new WinnerState(this);
this.count = numberGumballs;
if (numberGumballs > 0) {
state = noQuarterState;
}
this.location = location;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
state.insertQuarter();
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
state.ejectQuarter();
}
public void turnCrank() {
state.turnCrank();
state.dispense();
}
void setState(State state) {
this.state = state;
}
void releaseBall() {
System.out.println("A gumball comes rolling out the slot...");
if (count != 0) {
count = count - 1;
}
}
public void refill(int count) {
this.count = count;
state = noQuarterState;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public State getState() {
return state;
}
public String getLocation() {
return location;
}
public State getSoldOutState() {
return soldOutState;
}
public State getNoQuarterState() {
return noQuarterState;
}
public State getHasQuarterState() {
return hasQuarterState;
}
public State getSoldState() {
return soldState;
}
public State getWinnerState() {
return winnerState;
}
public String toString() {
StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer();
result.append("\nMighty Gumball, Inc.");
result.append("\nJava-enabled Standing Gumball Model #2014");
result.append("\nInventory: " + count + " gumball");
if (count != 1) {
result.append("s");
}
result.append("\n");
result.append("Machine is " + state + "\n");
return result.toString();
}
}- 원격 통신을 응답받는 GumbleMachine 객체 구현입니다.
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
public class GumballMonitor {
GumballMachineRemote machine;
public GumballMonitor(GumballMachineRemote machine) {
this.machine = machine;
}
public void report() {
try {
System.out.println("Gumball Machine: " + machine.getLocation());
System.out.println("Current inventory: " + machine.getCount() + " gumballs");
System.out.println("Current state: " + machine.getState());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}- GumballMachine 정보를 파악하기 위한 원격 모니터링 객체 구현입니다.
테스트
public class GumballMachineTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GumballMachineRemote gumballMachine = null;
int count;
if (args.length < 2) {
System.out.println("GumballMachine <name> <inventory>");
System.exit(1);
}
try {
count = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
gumballMachine =
new GumballMachine(args[0], count);
Naming.rebind("//" + args[0] + "/gumballmachine", gumballMachine);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}//terminal
//rmiregistry를 먼저 실행
>> rmiregistry
//austin지역의 100개의 볼을 생성
>> java GuballMachineTestDrive austin.mightygumball.com 100모니터링 테스트 코드
import java.rmi.Naming;
public class GumballMonitorTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//모니터링할 위치
String[] location = {"rmi://santafe.mightygumball.com/gumballmachine",
"rmi://boulder.mightygumball.com/gumballmachine",
"rmi://austin.mightygumball.com/gumballmachine"};
if (args.length >= 0)
{
location = new String[1];
location[0] = "rmi://" + args[0] + "/gumballmachine";
}
GumballMonitor[] monitor = new GumballMonitor[location.length];
for (int i=0;i < location.length; i++) {
try {
GumballMachineRemote machine =
(GumballMachineRemote) Naming.lookup(location[i]);
monitor[i] = new GumballMonitor(machine);
System.out.println(monitor[i]);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
for (int i=0; i < monitor.length; i++) {
monitor[i].report();
}
}
}
2.가상 프록시(보호 프록시)

- 가상 프록시는 객체를 생성하는데 많은 비용이 드는 객체를 대신 생성하는 프록시 패턴입니다.
- 진짜 객체의 사용 호출을 호출 시점까지 최대한 미루는것을 통해 성능적인 부분에서 이점을 가져올수 있다.
가상 프록시 구현
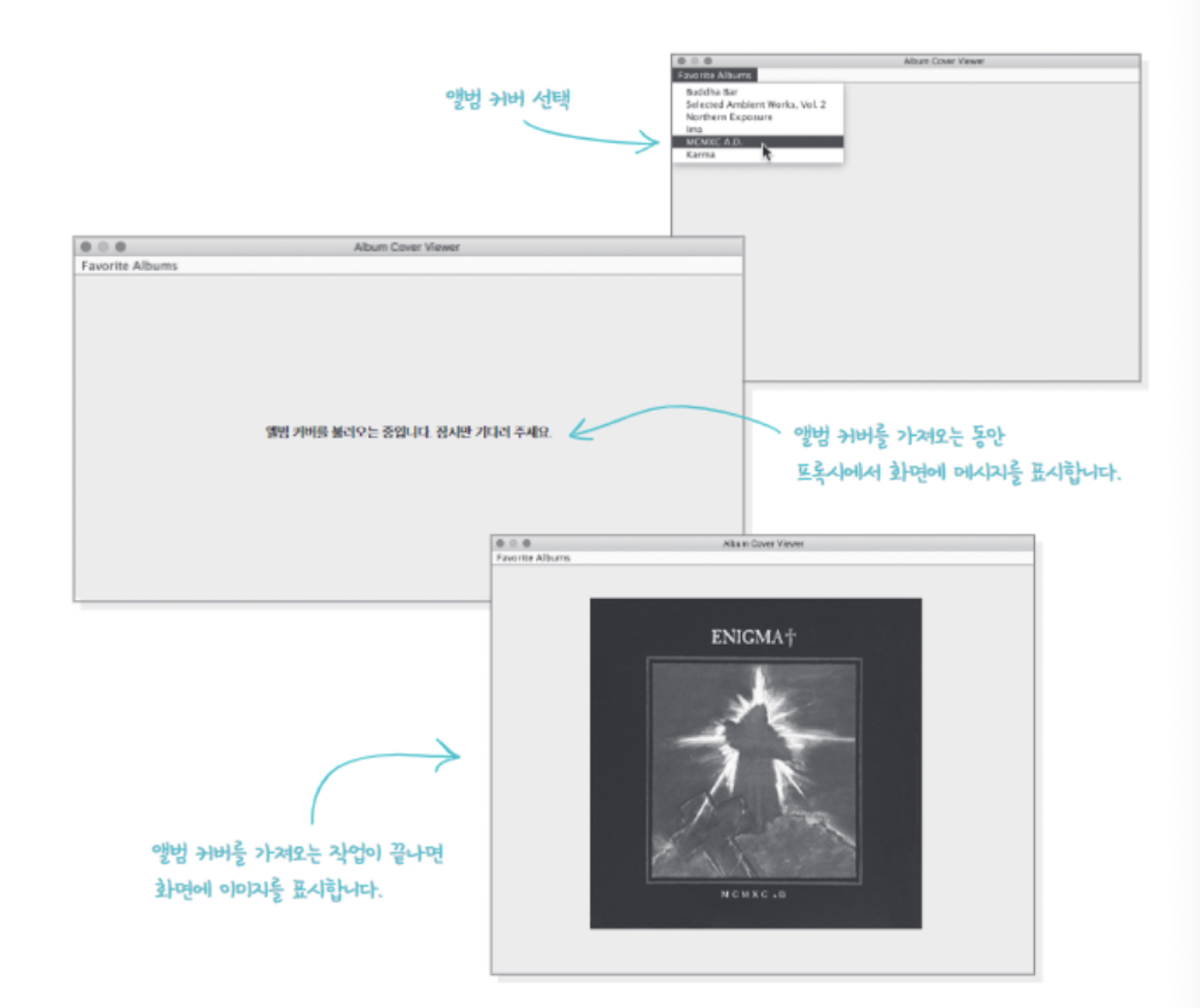
가상 프록시 이해를 위한 간단한 문제 제안
- 뮤직 서비스에서 음악을 조회할때 앨범의 커버 이미지를 가져옵니다.
- 앨범을 조회할 때까지는 앨범 커버 이미지를 불러올 필요가 없습니다. 그러나 앨범 커머 이미지를 가져오는데 다른 이미지를 사용자에게 보여줘야 합니다.
- 가상 프록시가 앨범 이미지를 가져오는동안 가상 프록시를 활용하여 “앨범 커버 이미지를 불러오는중입니다” 라는 이미지를 보여주는 예제를 만들어보도록 하겠습니다
가상 프록시 설계하기
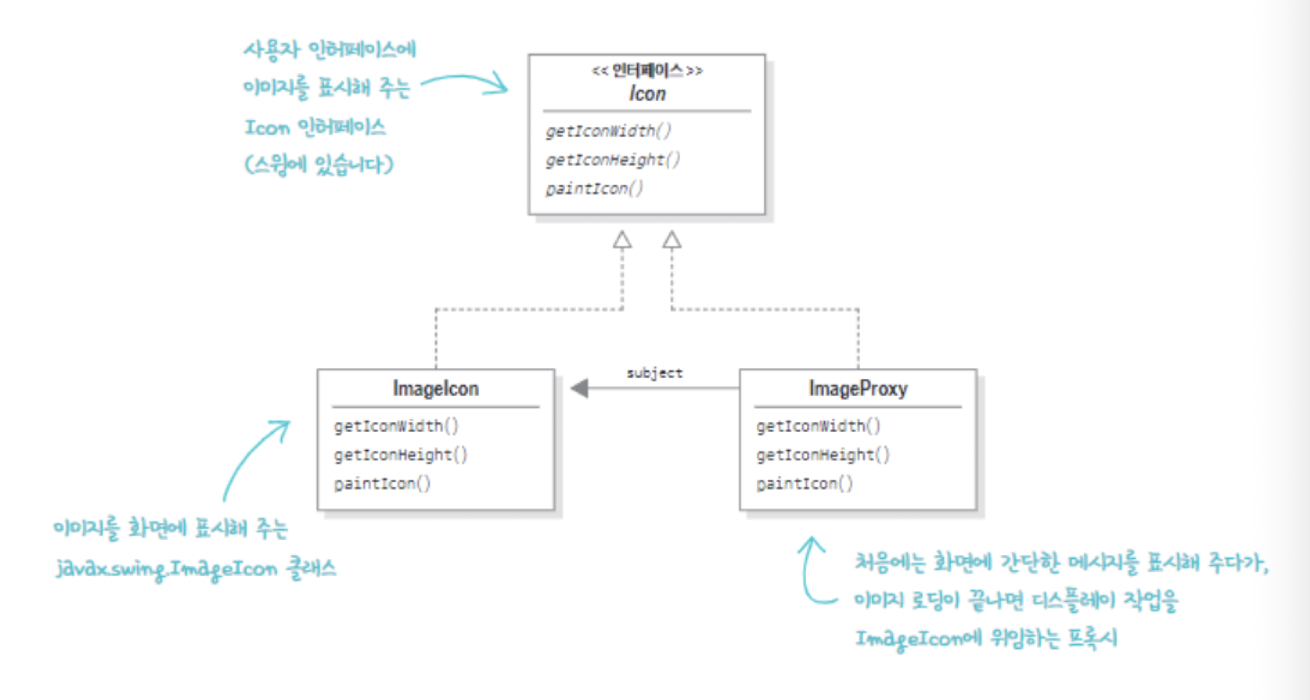
가상 프록시 구현
public interface Icon {
void paintIcon(Component var1, Graphics var2, int var3, int var4);
int getIconWidth();
int getIconHeight();
}- java에서 제공하는 Icon인터페이스 입니다.
class ImageProxy implements Icon {
//ImageIcon은 이미지 로딩이 끝났을 때 실제 이미지를 화면에 표시하는 아이콘 객체입니다.
//volatile을 사용해서 멀티 스레드 작업시 읽기를 보호하는 작업을 수행함
volatile ImageIcon imageIcon;
final URL imageURL;
Thread retrievalThread;
boolean retrieving = false;
public ImageProxy(URL url) { imageURL = url; }
//ImageIcon 로딩이 끝나기 전까지는 기본 높이 800를 리턴합니다.
public int getIconWidth() {
if (imageIcon != null) {
return imageIcon.getIconWidth();
} else {
return 800;
}
}
//ImageIcon 로딩이 끝나기 전까지는 기본 너비 600을 리턴합니다.
public int getIconHeight() {
if (imageIcon != null) {
return imageIcon.getIconHeight();
} else {
return 600;
}
}
//ImageIcon은 2개의 서로 다른 스레드에서사용합니다. 따라선 ImageIcon 변수를 volatile로 선언합니다.
//volatile을 사용해서 읽기를 보호하고 쓰기를 보호하기 위해 Setter메소드에 synchronized를 선언합니다.
synchronized void setImageIcon(ImageIcon imageIcon) {
this.imageIcon = imageIcon;
}
public void paintIcon(final Component c, Graphics g, int x, int y) {
if (imageIcon != null) {
imageIcon.paintIcon(c, g, x, y);
} else {
g.drawString("Loading album cover, please wait...", x+300, y+190);
if (!retrieving) {
retrieving = true;
retrievalThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
setImageIcon(new ImageIcon(imageURL, "Album Cover"));
//비동기 방식으로 계속 화면을 재갱신하여 imageurl을 계속 찾는 작업 수행
c.repaint();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
retrievalThread.start();
}
}
}
}- ImageProxy는 Icon 인터페이스를 구현합니다.
class ImageComponent extends JComponent {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Icon icon;
public ImageComponent(Icon icon) {
this.icon = icon;
}
public void setIcon(Icon icon) {
this.icon = icon;
}
public void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
super.paintComponent(g);
int w = icon.getIconWidth();
int h = icon.getIconHeight();
int x = (800 - w)/2;
int y = (600 - h)/2;
icon.paintIcon(this, g, x, y);
}
}- Pannel 정보를 담고있는 ImageComponent 구현입니다
테스트
public class ImageProxyTestDrive {
ImageComponent imageComponent;
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Album Cover Viewer");
JMenuBar menuBar;
JMenu menu;
Hashtable<String, String> albums = new Hashtable<String, String>();
public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {
ImageProxyTestDrive testDrive = new ImageProxyTestDrive();
}
public ImageProxyTestDrive() throws Exception {
albums.put("Buddha Bar","http://images.amazon.com/images/P/B00009XBYK.01.LZZZZZZZ.jpg");
albums.put("Ima","http://images.amazon.com/images/P/B000005IRM.01.LZZZZZZZ.jpg");
albums.put("Karma","http://images.amazon.com/images/P/B000005DCB.01.LZZZZZZZ.gif");
albums.put("MCMXC a.D.","http://images.amazon.com/images/P/B000002URV.01.LZZZZZZZ.jpg");
albums.put("Northern Exposure","http://images.amazon.com/images/P/B000003SFN.01.LZZZZZZZ.jpg");
albums.put("Selected Ambient Works, Vol. 2","http://images.amazon.com/images/P/B000002MNZ.01.LZZZZZZZ.jpg");
URL initialURL = new URL((String)albums.get("Selected Ambient Works, Vol. 2"));
menuBar = new JMenuBar();
menu = new JMenu("Favorite Albums");
menuBar.add(menu);
frame.setJMenuBar(menuBar);
for (Enumeration<String> e = albums.keys(); e.hasMoreElements();) {
String name = (String)e.nextElement();
JMenuItem menuItem = new JMenuItem(name);
menu.add(menuItem);
menuItem.addActionListener(event -> {
imageComponent.setIcon(new ImageProxy(getAlbumUrl(event.getActionCommand())));
frame.repaint();
});
}
// set up frame and menus
Icon icon = new ImageProxy(initialURL);
imageComponent = new ImageComponent(icon);
frame.getContentPane().add(imageComponent);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(800,600);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
URL getAlbumUrl(String name) {
try {
return new URL((String)albums.get(name));
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}가상 프록시 패턴과 데코레이터 패턴의 차이점
- 가상 프록시는 수행 결과를 먼저 받는 데코레이터 아니냐는 의구심이 생길수있습니다.
- 하지만 가상 프록시 패턴과 데코레이터 패턴은 용도로 구분이 가능합니다.
- 데코레이터 패턴은 새로운 행동을 추가하는 용도로 사용되지만 가상 프록시패턴은 어떤 클래스로 접근을 하는지 제어하는 용도로 사용됩니다.
3.보호 프록시
- 동적 프록시는 위와 같이 동작합니다.
- 이러한 동적프록시를 활용해서 보호프록시를 구현해보도록하겠습니다.
- 보호 프록시란 접근 권한을 바탕으로 객체로의 접근을 제어하는 프록시입니다.
보호 프록시 구현
보호 프록시 이해를 위한 간단한 문제 제안
- 데이팅 서비스를 개발하려고합니다.
- 데이팅 서비스는 서로 상대방의 괴짜 지수(좋은 쪽으로 얼마나 괴짜인지를 따지는 점수)를 매기는 기능을 사용하여 사용자들이 적극적으로 데이트 매칭이 이뤄질수 있도록 유도할려고합니다.
- 이때 사용자들이 서로 자신의 괴짜 지수를 함부로 바꾸지 못하게 보호 프록시를 사용해서 구현해보도록 하겠습니다.
public interface Person {
String getName();
String getGender();
String getInterests();
int getGeekRating();
void setName(String name);
void setGender(String gender);
void setInterests(String interests);
void setGeekRating(int rating);
}- 사람에 대한 인터페이스 정의입니다.
- setGeekRating은 점수를 인자로 받아 해당 사람의 괴짜 지수를 이동 평균 방식으로 계산합니다.
public class PersonImpl implements Person {
String name;
String gender;
String interests;
int rating;
int ratingCount = 0;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public String getInterests() {
return interests;
}
public int getGeekRating() {
if (ratingCount == 0) return 0;
return (rating/ratingCount);
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public void setInterests(String interests) {
this.interests = interests;
}
public void setGeekRating(int rating) {
this.rating += rating;
ratingCount++;
}
}- Person 인터페이스에대한 구현입니다.
public class OwnerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
Person person;
public OwnerInvocationHandler(Person person) {
this.person = person;
}
//InvocationHandler가 제공하는 Invoke 메소드
//Proxy는 호출하는 Proxy 자체 오브젝트를 의미, Method는 사용되어지 Method를 의미, args는 넘어온 매개변수의 정보를 의미
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws IllegalAccessException {
try {
//메소드 이름별로 수행 분기 로직
if (method.getName().startsWith("get")) {
return method.invoke(person, args);
//자신 계정의 GeekRating은 커스터 마이징 하면안되므로 접근시 예외처리 작업 수행
} else if (method.getName().equals("setGeekRating")) {
throw new IllegalAccessException();
} else if (method.getName().startsWith("set")) {
return method.invoke(person, args);
}
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}- 자신 계정의 소유권을 의미하는 Proxy Handler인 OwnerInvoactionHandelr를 구현합니다.
public class NonOwnerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
Person person;
public NonOwnerInvocationHandler(Person person) {
this.person = person;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws IllegalAccessException {
try {
if (method.getName().startsWith("get")) {
return method.invoke(person, args);
} else if (method.getName().equals("setGeekRating")) {
return method.invoke(person, args);
//소유권이 없으므로 객체의 set 작업은 모두 막아야함.
} else if (method.getName().startsWith("set")) {
throw new IllegalAccessException();
}
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}- 소유권이 없는 경우 InvocationHandelr을 구현합니다.
테스트
public class MatchMakingTestDrive {
HashMap<String, Person> datingDB = new HashMap<String, Person>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
MatchMakingTestDrive test = new MatchMakingTestDrive();
test.drive();
}
public MatchMakingTestDrive() {
initializeDatabase();
}
public void drive() {
Person joe = getPersonFromDatabase("Joe Javabean");
Person ownerProxy = getOwnerProxy(joe);
System.out.println("Name is " + ownerProxy.getName());
ownerProxy.setInterests("bowling, Go");
System.out.println("Interests set from owner proxy");
try {
ownerProxy.setGeekRating(10);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Can't set rating from owner proxy");
}
System.out.println("Rating is " + ownerProxy.getGeekRating());
Person nonOwnerProxy = getNonOwnerProxy(joe);
System.out.println("Name is " + nonOwnerProxy.getName());
try {
nonOwnerProxy.setInterests("bowling, Go");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Can't set interests from non owner proxy");
}
nonOwnerProxy.setGeekRating(3);
System.out.println("Rating set from non owner proxy");
System.out.println("Rating is " + nonOwnerProxy.getGeekRating());
}
Person getOwnerProxy(Person person) {
//Proxy 클래스에 있는 newProxyInstance를 사용하여 Proxy를 생성한다. 사용할 객체의 클래스. 인터페이스, InvocationHandler 정보를 매개변수 주고 생성한다.
return (Person) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
person.getClass().getClassLoader(),
person.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new OwnerInvocationHandler(person));
}
Person getNonOwnerProxy(Person person) {
return (Person) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
person.getClass().getClassLoader(),
person.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new NonOwnerInvocationHandler(person));
}
Person getPersonFromDatabase(String name) {
return (Person)datingDB.get(name);
}
void initializeDatabase() {
Person joe = new PersonImpl();
joe.setName("Joe Javabean");
joe.setInterests("cars, computers, music");
joe.setGeekRating(7);
datingDB.put(joe.getName(), joe);
Person kelly = new PersonImpl();
kelly.setName("Kelly Klosure");
kelly.setInterests("ebay, movies, music");
kelly.setGeekRating(6);
datingDB.put(kelly.getName(), kelly);
}
}프록시 패턴 UML
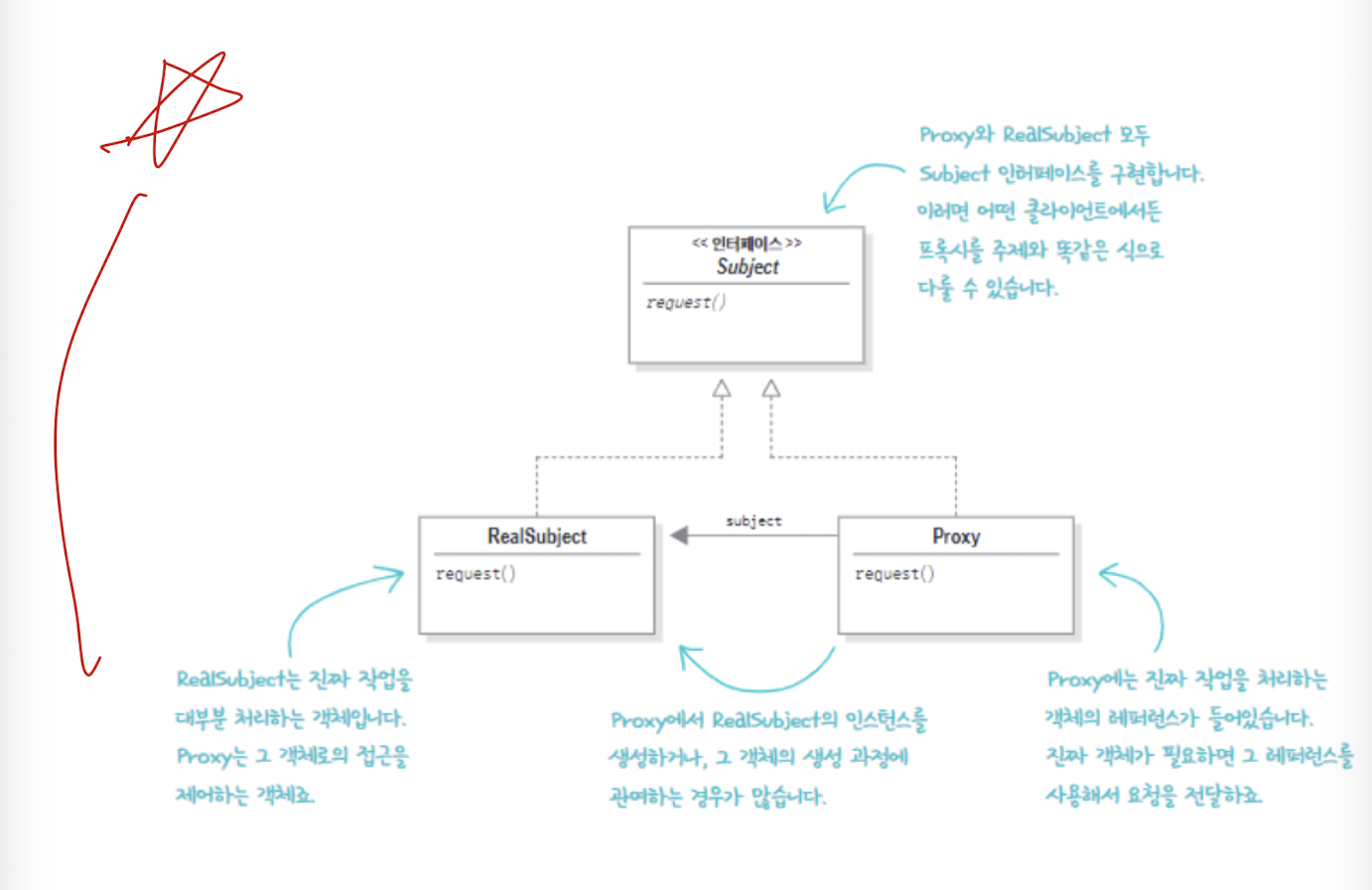
- UML은 크게 Subject, RealSubject, Proxy 3가지로 이루어집니다.
- RealSubject, Proxy 모두 Subject를 상속받아서 정의합니다.
- 진짜 작업은 RealSubject가 수행합니다. 그러나 Client는 Proxy를 사용해서 RealSubject를 호출합니다.
- Proxy는 객체의 대변인 역할을 하며 실제 객체를 수행해야할 때는 RealSubject의 레퍼런스를 사용해서 호출합니다.
- 이러한 형식을 통해 접근자가 RealSubject의 호출을 시도할 때 Proxy에서 검증하여 접근자를 차단하고 허용하는 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다.
정리
- 프록시 패턴은 특정 객체로의 접근을 제어하는 대리인을 제공합니다.
- 원격 프록시는 클라이언트와 원격 객체 사이의 데이터 전달을 관리합니다.
- 가상 프록시는 인스턴스를 만드는데 많은 비용이 드는 객체로의 접근을 제어합니다.
- 보호 프록시는 호출하는 쪽의 권한에 따라서 객체에 있는 메소드로의 접근을 제어합니다.
- 자바에 내장된 프록시 지원 기능을 사용하여 동적 프록시 클래스를 만들어서 원하는 핸들러에서 호출을 처리하도록 할 수 있습니다.
반응형
'디자인 패턴' 카테고리의 다른 글
| CHAPTER 13.실전 디자인 패턴 (0) | 2023.05.06 |
|---|---|
| CHAPTER 12.복합 패턴 (0) | 2023.05.06 |
| CHAPTER 10.상태 패턴 (0) | 2023.05.06 |
| CHAPTER 09.반복자 패턴과 컴포지트 패턴 (0) | 2023.05.06 |
| CHAPTER 08.템플릿 메소드 패턴 (0) | 2023.05.06 |
